Step into the future
with ZRIKA
We bridge the gap between your financial goals and innovative tools, delivering smart solutions for a seamless banking experience.













We bridge the gap between your financial goals and innovative tools, delivering smart solutions for a seamless banking experience.


Seamless banking solutions tailored for your everyday needs
Transfer funds securely in real time.
Accept payments via UPI, IMPS, bank transfers, and more
Enhance efficiency and reduce transportation costs
Process payments across borders with ease
Advanced fraud detection tools and end-to-end encryption
Digital KYC & Onboarding of Merchants

Process payments around the clock without delays
Empowering Business Transactions with Seamless Payment Solutions

ZriCrest offers an unparalleled and future-proof 'Corporate Card Solution' that redefines the meaning of Expense Management. It is an AI-powered program for Corporates to handle both business and personal expenses seamlessly.

A futuristic digital hub with interconnected nodes representing banks, merchants, fintechs, and other financial stakeholders(including government bodies), symbolising seamless collaboration and innovation.We are your Technology Service Provider (TSP), crafting bespoke software solutions that cater to the diverse needs of stakeholders in thefinancial ecosystem.

A dynamic switching platform that facilitates interoperability between different financial networks and systems.Ensures fast, secure, and reliable transaction processing across multiple platforms, enhancing overall operational efficiency.

Merchant Pay-In Solutions is a financial services and tools designed to help merchants (businesses or retailers) receive payments from customers. These solutions focus on facilitating secure, efficient, and convenient payment acceptance across various channels, including online, in-store, and mobile platforms.Merchant payments refer to transactions where a customer pays a merchant for goods or services using a payment method such as cash, credit/debit card, digital wallet, or bank transfer.

Merchant Pay-Out Solutions is a services and systems designed to help businesses disburse payments efficiently, securely, and reliably. These solutions focus on enabling merchants to transfer funds to various recipients, such as vendors, employees, customers, or partners, through automated and streamlined processes.
Core Banking systems, Customer Apps and Fraud Prevention tools.
POS integrations, Payment Tracking and Loyalty programs.
Expense management, Fleet management.
APIs, SDKs, and ready to deploy financial modules.
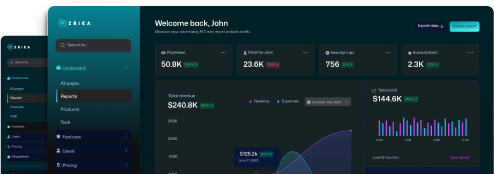





Unlock the Future of Banking with Smart, Secure, and Instant Access.
info@zrika.com
Solution We Offer
Copyright © 2025 NEXNEBULA TECHNOLOGIES PRIVATE LIMITED. All Rights Reserved.